Analyst says WCS price boost reflects global shortage
By Will Gibson
Follow CEC on Linkedin CEC Linkedin
Follow CEC on Facebook CEC Facebook
Follow CEC on Twitter CEC Twitter

Worker at an oil sands SAGD well pad in northern Alberta. Photo courtesy Strathcona Resources
Once priced at a steep discount to its lighter, sweeter counterparts, Canadian oil has earned growing admiration—and market share—among new customers in Asia.
Canada’s oil exports are primarily “heavy” oil from the Alberta oil sands, compared to oil from more conventional “light” plays like the Permian Basin in the U.S.
One way to think of it is that heavy oil is thick and does not flow easily, while light oil is thin and flows freely, like fudge compared to apple juice.
“The refining industry wants heavy oil. We are actually in a shortage of heavy oil globally right now, and you can see that in the prices,” said Susan Bell, senior vice-president of downstream research with Rystad Energy.
A narrowing price gap
Alberta’s heavy oil producers generally receive a lower price than light oil producers, partly a result of different crude quality but mainly because of the cost of transportation, according to S&P Global.
The “differential” between Western Canadian Select (WCS) and West Texas Intermediate (WTI) blew out to nearly US$50 per barrel in 2018 because of pipeline bottlenecks, forcing Alberta to step in and cut production.
So far this year, the differential has narrowed to as little as US$10 per barrel, averaging around US$12, according to GLJ Petroleum Consultants.
“The differential between WCS and WTI is the narrowest I’ve seen in three decades working in the industry,” Bell said.
Trans Mountain Expansion opens the door to Asia

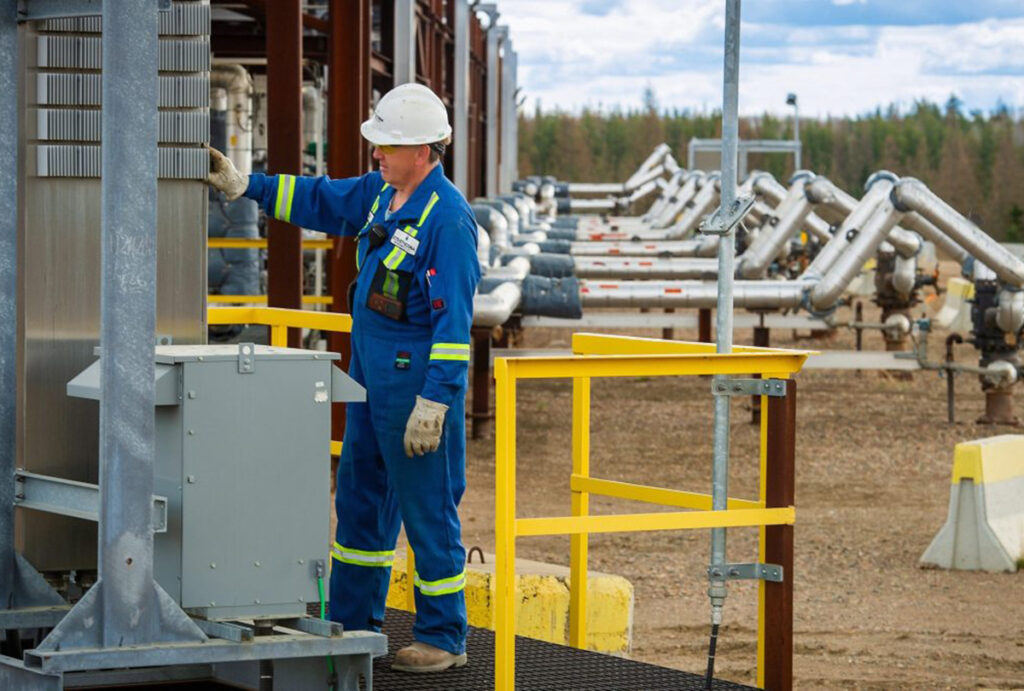
Oil tanker docked at the Westridge Marine Terminal in Burnaby, B.C. Photo courtesy Trans Mountain Corporation
The price boost is thanks to the Trans Mountain expansion, which opened a new gateway to Asia in May 2024 by nearly tripling the pipeline’s capacity.
This helps fill the supply void left by other major regions that export heavy oil – Venezuela and Mexico – where production is declining or unsteady.
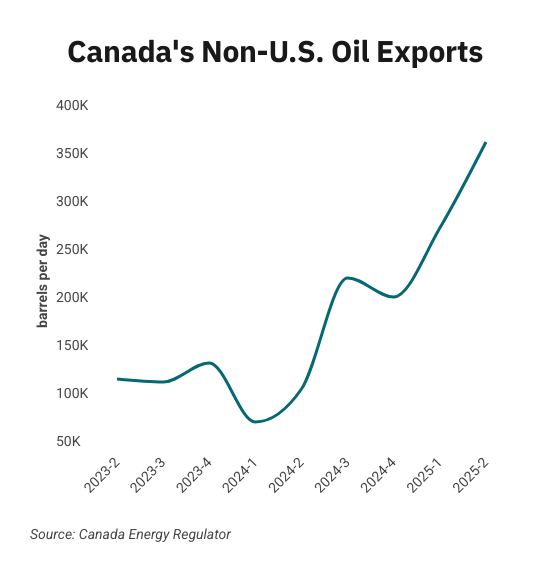
Canadian oil exports outside the United States reached a record 525,000 barrels per day in July 2025, the latest month of data available from the Canada Energy Regulator.
China leads Asian buyers since the expansion went into service, along with Japan, Brunei and Singapore, Bloomberg reports.
Asian refineries see opportunity in heavy oil
“What we are seeing now is a lot of refineries in the Asian market have been exposed long enough to WCS and now are comfortable with taking on regular shipments,” Bell said.
Kevin Birn, chief analyst for Canadian oil markets at S&P Global, said rising demand for heavier crude in Asia comes from refineries expanding capacity to process it and capture more value from lower-cost feedstocks.
“They’ve invested in capital improvements on the front end to convert heavier oils into more valuable refined products,” said Birn, who also heads S&P’s Center of Emissions Excellence.
Refiners in the U.S. Gulf Coast and Midwest made similar investments over the past 40 years to capitalize on supply from Latin America and the oil sands, he said.
While oil sands output has grown, supplies from Latin America have declined.
Mexico’s state oil company, Pemex, reports it produced roughly 1.6 million barrels per day in the second quarter of 2025, a steep drop from 2.3 million in 2015 and 2.6 million in 2010.
Meanwhile, Venezuela’s oil production, which was nearly 2.9 million barrels per day in 2010, was just 965,000 barrels per day this September, according to OPEC.
The case for more Canadian pipelines

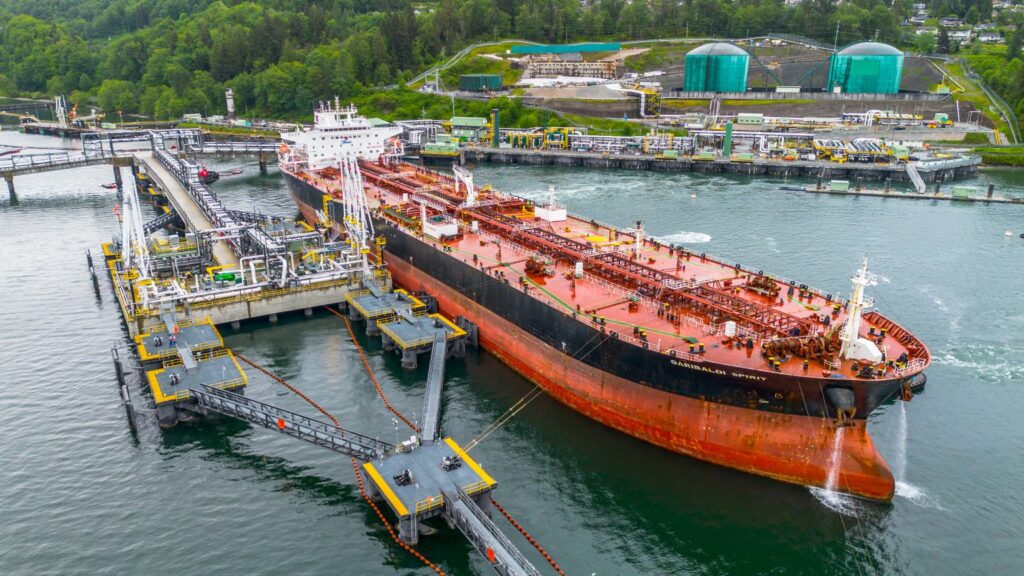
Worker at an oil sands SAGD processing facility in northern Alberta. Photo courtesy Strathcona Resources
“The growth in heavy demand, and decline of other sources of heavy supply has contributed to a tighter market for heavy oil and narrower spreads,” Birn said.
Even the International Energy Agency, known for its bearish projections of future oil demand, sees rising global use of extra-heavy oil through 2050.
The chief impediments to Canada building new pipelines to meet the demand are political rather than market-based, said both Bell and Birn.
“There is absolutely a business case for a second pipeline to tidewater,” Bell said.
“The challenge is other hurdles limiting the growth in the industry, including legislation such as the tanker ban or the oil and gas emissions cap.”
A strategic choice for Canada
Because Alberta’s oil sands will continue a steady, reliable and low-cost supply of heavy oil into the future, Birn said policymakers and Canadians have options.
“Canada needs to ask itself whether to continue to expand pipeline capacity south to the United States or to access global markets itself, which would bring more competition for its products.”
The unaltered reproduction of this content is free of charge with attribution to Canadian Energy Centre Ltd.
Share This:




 CDN NEWS |
CDN NEWS |  US NEWS
US NEWS