This marks a major turnaround for the industry, which is trying to persuade investors to stick with it despite mounting concerns about climate change. Until recently, both companies were focused on paying down debt and strengthening their balance sheets in the aftermath of the oil slump caused by the coronavirus pandemic.
What’s changed is a broad rally in commodity prices, in which the surge in crude has been matched or exceeded by natural gas, metals and other bulk raw materials. It’s not just Shell and Total returning money to shareholders, almost every natural resources group from Rio Tinto Plc to Anglo American Plc is either raising dividends or buying back shares.
“We wanted to signal to the market the confidence that we have in cash flows,” Shell Chief Executive Officer Ben van Beurden said on a conference call. In the oil market “supply is going to be constrained and demand is actually quite strong.”
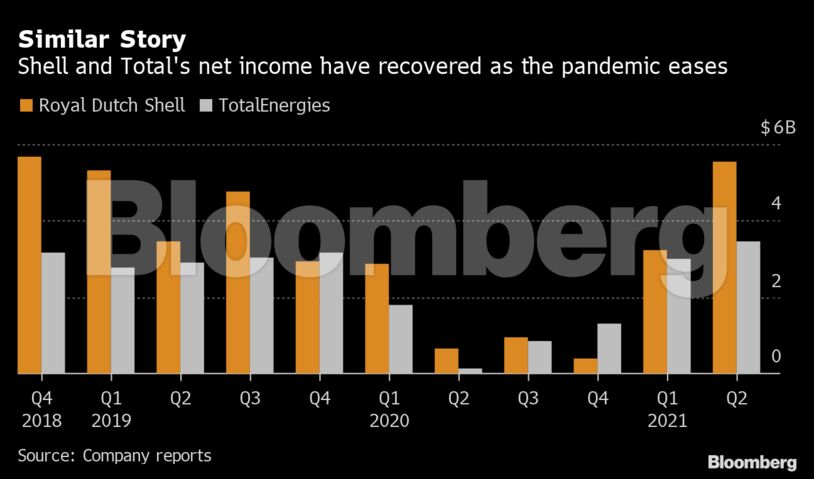
Shell and TotalEnergies both reported big surges in adjusted net income and cash flow for the second quarter, taking the figures back to pre-pandemic levels. That had been largely expected by analysts, but the big improvement in shareholder returns caught them by surprise.
”We knew Shell was set to raise distributions today, but the scale of the increase is significantly above expectations,” Redburn analyst Stuart Joyner said in a note.
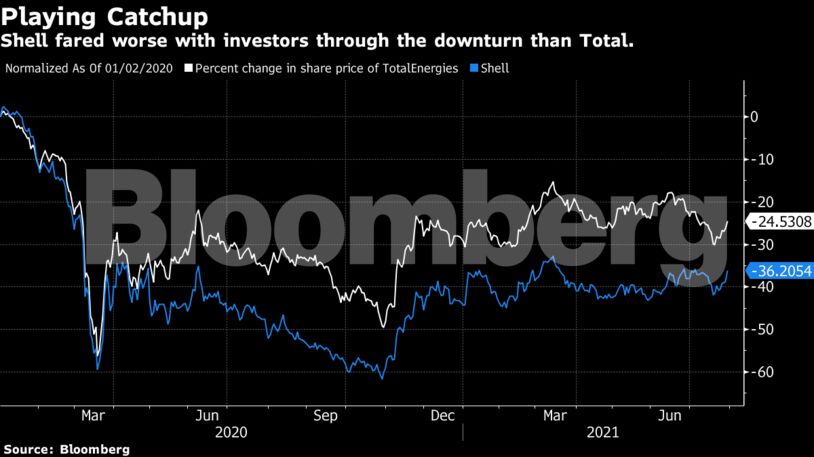
Shell has some catching up to do. Last year, it cut its dividend by two-thirds during the depths of the Covid-19 lockdowns. Modest increases to the payout since then did little to boost the company’s appeal, with its market value today still more than a third below pre-pandemic levels despite a full recovery in oil prices.
TotalEnergies, which entered the Covid-19 crisis with less debt and maintained its payout throughout the downturn, has fared better with investors. The French company may buy back as much as $800 million of its shares by the end of the year, assuming oil averages $66 a barrel, and as much as $1 billion if it averages $68, Chief Executive Officer Patrick Pouyanne said on a conference call.
The dividend will grow only when it’s backed by a “structural increase” in cash flow stemming from additional energy production and sales, Pouyanne said.
Other European oil majors are taking a similar approach. BP Plc and Equinor ASA have already made incremental dividend increases and announced more modest buyback plans.
Wooing investors has seldom been more important for Big Oil. The industry is under increasing pressure to turn away from fossil fuels and embrace clean energy as the world grapples with the evident dangers of a warming planet. Most of the European majors have laid out broad plans to achieve net-zero emissions by the middle of the century, but there are questions about how much it will cost and whether profits from renewable energy can match oil and gas.
These doubts have weighed on the industry’s valuation, which overall is still 22% below its level at the end of 2019, said Banco Santander SA analyst Jason Kenney. A period of strong profits and cash flow will make it much easier for these companies to make the transition to clean energy while keeping investors on board.
“The climate crisis requires significant investment to truly shift to low and no carbon energy,” Kenney said. “But there is a huge wall of cash on the horizon from integrated energy companies in the second half of 2021 and certainly by 2022. And financial frames look credible and attractive at current levels.”
Share This:




 CDN NEWS |
CDN NEWS |  US NEWS
US NEWS